The previous subsection solve equation 3 in a poststack image domain (zero subsurface-offset). But a prestack regularization is necessary to reduce the noise in the inversion result. If subsurface offset is included in the computation of the Hessian, a generalization to the prestack image domain of equation 4 is possible.
Three different regularization schemes for wave-equation inversion have been discussed in the literature. First, an identity operator which is customary in many scientific applications (damping). Second, a geophysical regularization which penalizes the roughness of the image in the offset ray parameter dimension (which is equivalent the reflection angle dimension) Kuehl and Sacchi (2001); Prucha et al. (2000). Third, a differential semblance operator to penalize the energy in the image not focused at zero subsurface-offset Shen et al. (2003). In this paper I use the third regularization scheme, the regularization in the reflection angle domain.
A generalization to the prestack image domain of equation 3 needs regularization to obtain a stable solution. The first option for regularization is a customary damping that can be stated as follows:
| |
||
| (5) |
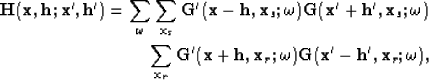 |
||
The third regularization option for the prestack generalization of equation 3, is penalizing the energy in the image not focused at zero subsurface-offset. This is obtained using the fitting goals,
| |
||
| (6) |
In the next section I compare the numerical solution of the inversion problems stated in equations 5 and 6 to the imaging of Sigsbee model.