




Next: Split-Step Fourier Approximation
Up: Acoustic wave-equation in 3D
Previous: Acoustic wave-equation in 3D
Developing an expression for the extrapolation wavenumber requires
isolating one of the wavenumbers in equation 11 (herein
assumed to be coordinate 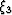 ). Rearranging the results of
expanding equation 11 by introducing indicies i,j=1,2,3
yields,
). Rearranging the results of
expanding equation 11 by introducing indicies i,j=1,2,3
yields,
| 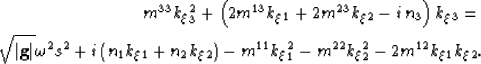 |
|
| (12) |
An expression for wavenumber 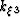 can be obtained by completing the
square,
can be obtained by completing the
square,
| 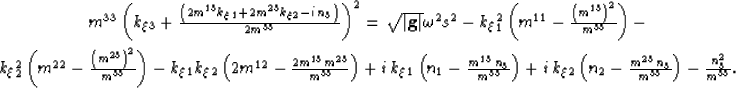 |
(13) |
| |
Isolating wavenumber 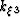 yields,
yields,
| ![\begin{displaymath}
k_\xi_3=
- a_1 k_\xi_1
- a_2 k_\xi_2
+ i a_3
\pm
\left[
a_...
... i\,k_\xi_1
+ a_9 i\,k_\xi_2
- a_{10}^2
\right]^{\frac{1}{2}},\end{displaymath}](img29.gif) |
(14) |
where ai are non-stationary coefficients given by,
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\mathbf{a}
=
\left[
\frac{g^{13}}{ g^{33}} \;\;\;\;\;
\frac{...
...}\right]\;\;\;\;\;
\frac{ n_3 }{ m^{33} }
\right]^{\mathbf{T}}.\end{displaymath}](img30.gif) |
(15) |
Note that the coefficients contain a mixture of mij and gij
terms, and that positive definite terms, a4, a5, a6 and a10
in equation 14, are
squared such that the familiar Cartesian split-step Fourier correction is
recovered below.





Next: Split-Step Fourier Approximation
Up: Acoustic wave-equation in 3D
Previous: Acoustic wave-equation in 3D
Stanford Exploration Project
4/5/2006
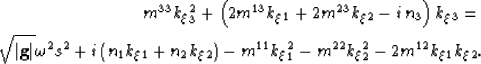
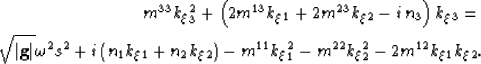
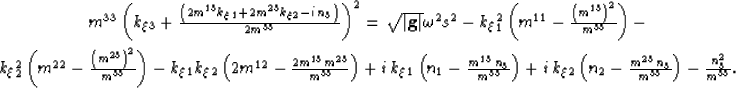
![\begin{displaymath}
\mathbf{a}
=
\left[
\frac{g^{13}}{ g^{33}} \;\;\;\;\;
\frac{...
...}\right]\;\;\;\;\;
\frac{ n_3 }{ m^{33} }
\right]^{\mathbf{T}}.\end{displaymath}](img30.gif)