




Next: Program functions
Up: Inversion objects
Previous: Operator
The base solver class, SEP.solv_base.solver,
is inherited from SEP.opt_base.options.
The solver keeps track of its progress using the
SEP.stat_sep.status module.
It expects that the parameters niter, the
number of iterations, and stepper,
the class that calculates the step to be set by
the time prep_run is called.
The function iter iterates niter times.
To make expanding the solver easier, it includes
a dummy function end_iter(iter)
that is run at the end of each iteration. This function
can be overwritten to do things like write out
the model at each iteration.
There are three classes derived from
the SEP.solv_base.solver class.
The SEP.solv_smp.solver class is
designed for solving problems of the form
| 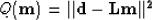 |
(1) |
where 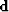 is the data,
is the data, 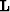 is the operator,
and
is the operator,
and 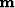 is the model.
It expects that its children set the operator op,
the data data, the model model
before its prep_run function is invoked.
It will also look for
a weighting operator wop, a
a model vector v, an initial model m0,
and an initial residual vector resd.
From this information, an initial residual model vector
are calculated and SEP.solv_base.solver's
prep_run is invoked.
is the model.
It expects that its children set the operator op,
the data data, the model model
before its prep_run function is invoked.
It will also look for
a weighting operator wop, a
a model vector v, an initial model m0,
and an initial residual vector resd.
From this information, an initial residual model vector
are calculated and SEP.solv_base.solver's
prep_run is invoked.
The SEP.solv_reg.solver class is also derived
from SEP.solv_base.solver class.
It is used for regularized inversion problems of
the form,
| 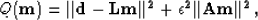 |
(2) |
where 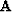 is the regularization operator.
It expects
all of the arguments of SEP.solv_smp.solver
with the
addition
of
regularization operator reg and the
relative weighting parameter
is the regularization operator.
It expects
all of the arguments of SEP.solv_smp.solver
with the
addition
of
regularization operator reg and the
relative weighting parameter  eps.
In addition accepts the optional residual model space
vector resm.
eps.
In addition accepts the optional residual model space
vector resm.
The final solver derived from SEP.solv_base.solver is
SEP.solve_prec.solver. It is used from regularized problems
with model preconditioning of the form,
| 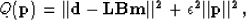 |
(3) |
where 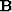 is the preconditioning operator and
is the preconditioning operator and 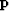 is the
preconditioned variable, where
is the
preconditioned variable, where 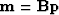 .It expects all of the same parameters of SEP.solv_reg.solver,
with reg removed and prec, the preconditioning operator,
added.
.It expects all of the same parameters of SEP.solv_reg.solver,
with reg removed and prec, the preconditioning operator,
added.
All of the solvers are currently linear solvers. Adding non-linear
solvers would be fairly easy.
They all require a step function. Currently only a
conjugate gradient step function is available in SEP.cgstep.cgstep.





Next: Program functions
Up: Inversion objects
Previous: Operator
Stanford Exploration Project
5/3/2005