Bortfeld's three term reflectivity equation is a linearized form of
the Zoeppritz equation. It predicts the amplitude (R) at various reflection
angles (![]() ) given three reflectivity terms. These three terms
are the zero-offset reflectivity (RO), the P-wave
reflectivity (RP), and a gradient term (Rsh). This is its basic form:
) given three reflectivity terms. These three terms
are the zero-offset reflectivity (RO), the P-wave
reflectivity (RP), and a gradient term (Rsh). This is its basic form:
| (1) |
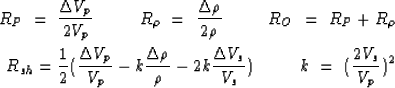 |
(2) | |
This form is easily obtained algebraically from the form derived in Aki and Richards (1980). Both forms are well known and frequently used, but may not be accurate in areas where the interval velocities are not well known. Therefore, we choose to look at a different form.