 |
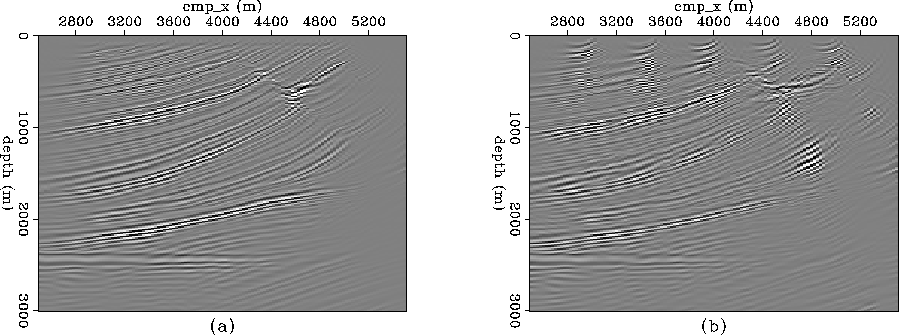
Figure 4 Migrated images produced with data having a fully-sampled shot axis (a), and a very sparsely-sampled shot axis (b).
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) , datasets
collected with sparse-shot geometries are most suitable for
shot-profile migration.
Figure
, datasets
collected with sparse-shot geometries are most suitable for
shot-profile migration.
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) compares the migrated (zero-offset) images of
the two prestack datasets.
The dataset that produced panel (a) had a fully-sampled shot axis,
while the shot axis on the dataset that produced panel (b) contained
only every twentieth shot.
Even with the very sparsely-sampled shot axis, the geologic structure
is clearly interpretable in Figure
compares the migrated (zero-offset) images of
the two prestack datasets.
The dataset that produced panel (a) had a fully-sampled shot axis,
while the shot axis on the dataset that produced panel (b) contained
only every twentieth shot.
Even with the very sparsely-sampled shot axis, the geologic structure
is clearly interpretable in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) (b).
(b).
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
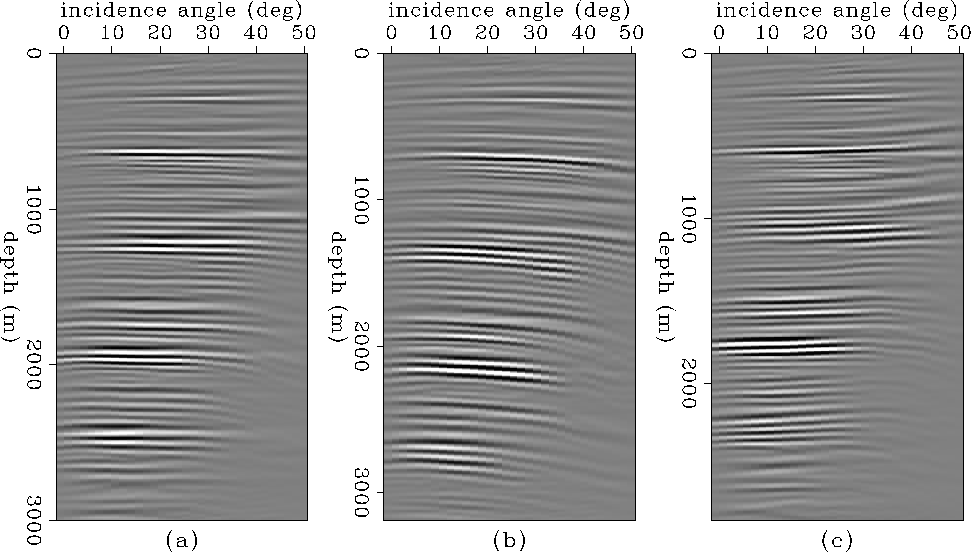
To illustrate the problems associated with sampling for shot-profile
migrations, Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows the same image
gathers as Figure
shows the same image
gathers as Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) , but after migrating only
every twentieth shot. Energy is no longer concentrated around
zero-offset.
, but after migrating only
every twentieth shot. Energy is no longer concentrated around
zero-offset.
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) (a) shows the equivalent picture in the
angle domain.
Even if though the velocity is correct and the zero-offset image
[Figure
(a) shows the equivalent picture in the
angle domain.
Even if though the velocity is correct and the zero-offset image
[Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) (b)] seems reasonable, coverage in the
angle-domain is very irregular.
When the velocities are incorrect, the angle gathers remain chaotic:
shot aliasing has effectively rendered the angle-gathers
uninterpretable in terms of velocities.
(b)] seems reasonable, coverage in the
angle-domain is very irregular.
When the velocities are incorrect, the angle gathers remain chaotic:
shot aliasing has effectively rendered the angle-gathers
uninterpretable in terms of velocities.
Although both de Bruin's 1990 original methodology and the approach described here provide means of obtaining common-image gathers from shot-profile migration, the problem of shot aliasing remains important for the geometries that are best suited to shot-profile migration.
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)