|
arraytest
Figure 1 Long Beach passive array. ``Mainline Shotpoints and Geophones'' denote the source and receiver locations for the USGS high-res survey (see text). Approximate locations of the well, drill-truck, and water pump are also shown. | 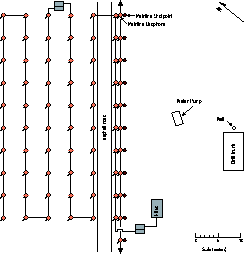 |
A manually triggered Geometrics RX-60 seismograph recorded 60 channels at a sample interval of 4 ms; no filters were used. Over two days, this passive experiment produced approximately 170 minutes of 10-second long records and 20 60-second long records. During each of the 60-second records, the first author performed a ``two footed'' stomp at one the geophones along the northeastern and southwestern edges of the array. The array also recorded energy from the intermittant operation of the nearby drill-bit, drill-truck engine, and the gasoline-powered water pump. Figure 2 shows five seconds of recorded data after notch-filtering.
|
arraytest
Figure 1 Long Beach passive array. ``Mainline Shotpoints and Geophones'' denote the source and receiver locations for the USGS high-res survey (see text). Approximate locations of the well, drill-truck, and water pump are also shown. |  |
|
strip
Figure 2 Five seconds of passive seismic data after notch-filtering. | 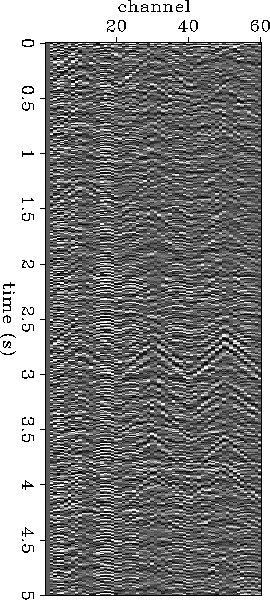 |