Next: About this document ...
Up: Appendix
Previous: Inversion of a 22
Using the preceding results, I can invert for the Hessian in
equation (9), either with or without regularization.
The fitting goal is
| 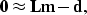 |
(28) |
with 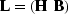 and
and 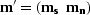 .The matrix equation we want to solve is
.The matrix equation we want to solve is
| 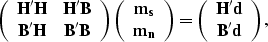 |
(29) |
where 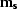 and
and 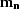 are the unknowns.
For
are the unknowns.
For 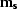 , I use the bottom row of equation (25).
For
, I use the bottom row of equation (25).
For 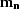 , I use the top row of equation (26).
We have, then,
, I use the top row of equation (26).
We have, then,
| 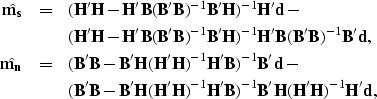 |
(30) |
| |
| (31) |
| |
which can be simplified as follows:
| 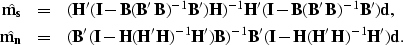 |
(32) |
| (33) |
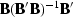 is the coherent noise resolution matrix,
whereas
is the coherent noise resolution matrix,
whereas  is the signal resolution
matrix. Denoting
is the signal resolution
matrix. Denoting 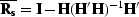 and
and 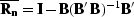 yields the following simplified expression for
yields the following simplified expression for 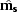 and
and
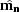 :
:
| 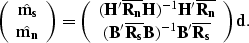 |
(34) |
- With model space regularization
The fitting goal becomes
| 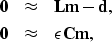 |
(35) |
| (36) |
with 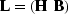 ,
, 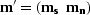 and
and
| 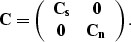 |
(37) |
The matrix equation we want to solve is
| 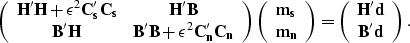 |
(38) |
Using equations (25) and (26) we obtain
| 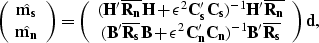 |
(39) |
where 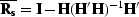 and
and 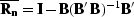 .
.





Next: About this document ...
Up: Appendix
Previous: Inversion of a 22
Stanford Exploration Project
4/29/2001