Data were generated using SEPlib Kirmod3d program. The
reflectivity map simply consists of a set of gradually dipping planes,
from zero dip to ![]() . The azimuth of the planes is
. The azimuth of the planes is ![]() with respect to the direction of the acquisition, which maximizes problems
in imaging.
with respect to the direction of the acquisition, which maximizes problems
in imaging.
|
planes
Figure 7 Geometry of the set of slanted planes, dipping at | 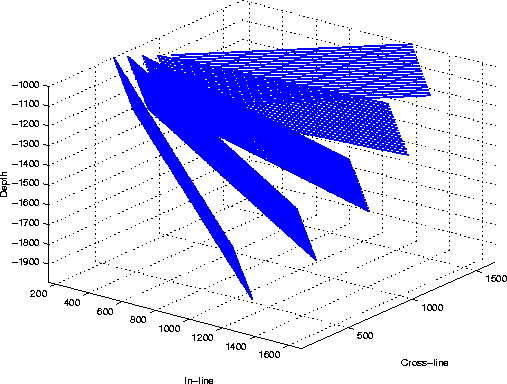 |
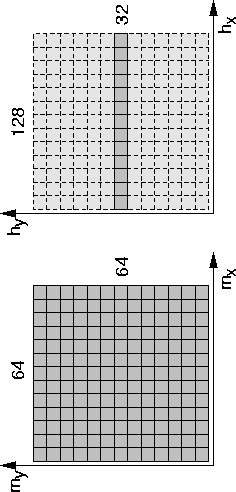
Data generated are on a regular grid and are common-azimuth, that is, with no cross-line offset component. The geometry of the grid is illustrated in Figure 8, with 64 samples in cmp-x and cmp-y, 128 in offset.
 |
We used a very fine time sampling (1 ms) in order to minimize interpolation errors during modeling with Kirmod3d and sub-sampled data to 2ms afterwards. We generated Green functions with velocity law v(z)=1500+0.5z, which roughly corresponds to typical gradients found in the Gulf of Mexico.