




Next: Migration effect
Up: AVO inversion
Previous: Modeling effect
We used model 1 to understand the effect of the overburden in the resulting
amplitudes. We compared the amplitudes of the 2-layer case to the
amplitudes in model 1, which includes an overburden zone with 2 flat layers
and a target zone encased in shale (see top of Figure 1).
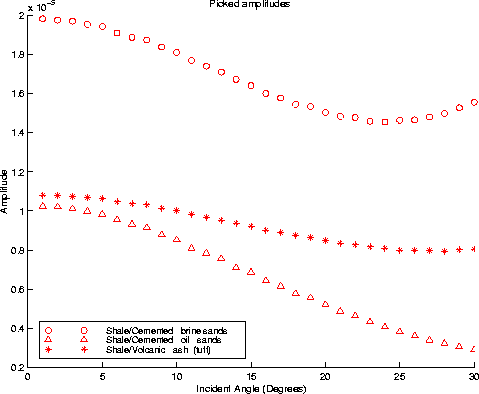
The picked amplitudes at the top of the target zone (2 km depth) are
plotted in Figure 9; note the good agreement with
the results illustrated in Figure 6 corresponding to the
2-layer case. The amplitudes in model 1 are slightly higher, which can
be expected because in this case the reflector appears at a higher time and
the spherical divergence correction that we are applied increases the
amplitudes more at a higher time (without the velocity taken into account).
To confirm this, we picked the amplitudes before any preprocessing and they
are identical at the near offset.
We also expected some differences at the far offsets due to the AVO effect
of the additional layers in model 1 (overburden effect).
Using Equation (2), we calculated the intercept (A) and gradient (B)
attributes
from the picked amplitudes in model 1 by
fitting the amplitude versus 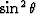 values to a straight-line
approximation using a least-squares curve fitting method.
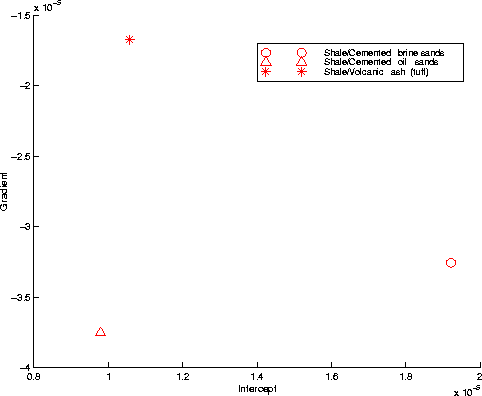
Figure 11 shows the crossplot
of the resulting intercept and gradient attributes; note the good quantitative
agreement with Figure 10, which illustrates the theoretical
values from Shuey's approximation.
values to a straight-line
approximation using a least-squares curve fitting method.
Figure 11 shows the crossplot
of the resulting intercept and gradient attributes; note the good quantitative
agreement with Figure 10, which illustrates the theoretical
values from Shuey's approximation.
model1pick
Figure 9 Picked amplitudes from model 1
|
|  |





ABshuey
Figure 10 Intercept versus Gradient crossplot
from Shuey's approximation of P-wave reflection coefficient
|
|  |





ABmodel1
Figure 11 Intercept versus Gradient
crossplot from picked amplitudes in data model 1 before migration
|
|  |










Next: Migration effect
Up: AVO inversion
Previous: Modeling effect
Stanford Exploration Project
4/28/2000
![]() values to a straight-line
approximation using a least-squares curve fitting method.
Figure 11 shows the crossplot
of the resulting intercept and gradient attributes; note the good quantitative
agreement with Figure 10, which illustrates the theoretical
values from Shuey's approximation.
values to a straight-line
approximation using a least-squares curve fitting method.
Figure 11 shows the crossplot
of the resulting intercept and gradient attributes; note the good quantitative
agreement with Figure 10, which illustrates the theoretical
values from Shuey's approximation.


