




Next: Example
Up: METHODOLOGY
Previous: Signal to noise separation
A PEF ( ) by definition is the filter that minimizes
the energy when convolved with the data (
) by definition is the filter that minimizes
the energy when convolved with the data (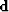 ).
To estimate a space-invariant filter, this amounts to applying the
fitting goal,
).
To estimate a space-invariant filter, this amounts to applying the
fitting goal,
| 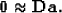 |
(7) |
When estimating a space-varying PEF, the number of filter coefficients
can quickly become more than the number of data points, creating
an underdetermined problem.
Crawley et al. (1999) proposed estimating space varying filter with
radial patch.
The
fitting goals become
| 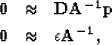 |
(8) |
| |
where 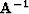 is a preconditioning operator that smoothes
in a radial direction (assuming that dips will be
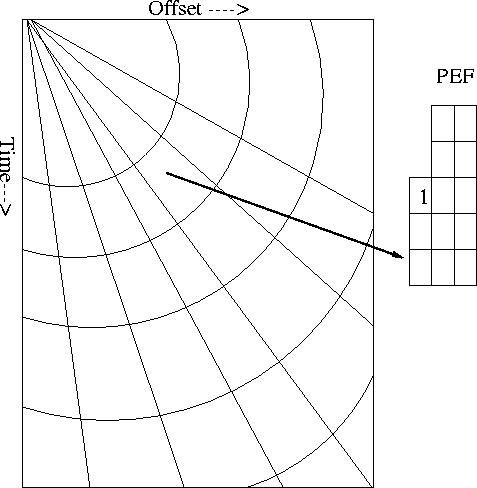
more consistent along radial lines, Figure 1.
is a preconditioning operator that smoothes
in a radial direction (assuming that dips will be
more consistent along radial lines, Figure 1.
pef
Figure 1 Space varying filter composition. A different filter is placed
inside each micro-patch. The filter estimation problem is
done globally, with the filter coefficient smoothed in a radial direction.
|
|  |






Next: Example
Up: METHODOLOGY
Previous: Signal to noise separation
Stanford Exploration Project
4/27/2000
![]() ) by definition is the filter that minimizes
the energy when convolved with the data (
) by definition is the filter that minimizes
the energy when convolved with the data (![]() ).
To estimate a space-invariant filter, this amounts to applying the
fitting goal,
).
To estimate a space-invariant filter, this amounts to applying the
fitting goal,
