




Next: Examples
Up: Fomel: 3-D plane waves
Previous: Factorizing plane waves
It may seem difficult to estimate the plane slope px for a
Lax-Wendroff filter of the form (10) because px appears
non-linearly in the filter coefficients. However, using the analytical
form of the filter, we can easily linearize it with respect to the
plane slope and set up a simple iterative scheme:
| 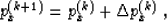 |
(11) |
where k stands for the iteration count, and 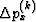 is found
from the linearized equation
is found
from the linearized equation
| 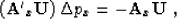 |
(12) |
where 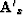 is the derivative of
is the derivative of 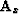 with respect to
px. To avoid unstable division by zero when solving equation
(12) for
with respect to
px. To avoid unstable division by zero when solving equation
(12) for 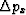 , Adding a regularization equation
, Adding a regularization equation
| 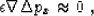 |
(13) |
where  is a small scalar regularization parameter, I solve
system (12-13) in the least-square sense to
obtain a smooth slope variation
is a small scalar regularization parameter, I solve
system (12-13) in the least-square sense to
obtain a smooth slope variation 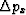 at each iteration. In
practice, iteration process (11) quickly converges to a
stable estimate of px.
at each iteration. In
practice, iteration process (11) quickly converges to a
stable estimate of px.





Next: Examples
Up: Fomel: 3-D plane waves
Previous: Factorizing plane waves
Stanford Exploration Project
10/25/1999