Next: Derivation of integral AMO
Up: Inversion to common offset
Previous: Migration after regularization
I have presented a new approach for imaging irregularly sampled 3D prestack
data. The method poses partial stacking with AMO as an optimization process to
reduce the size of prestack data and regularize its coverage before
migration.
The new inversion, named ICO is applied to normal-moveout corrected
data. It enables prestack analysis of the reflectivity function since
the output models are partial stacks at non-zero offset. The partial
stacks can be migrated separately and, either stacked together to
form the final image, or, individually analyzed for amplitude and
velocity variations.
I have presented a cost effective implementation of ICO in the Log-stretch
Fourier domain with proper preconditioning and regularization of the
inversion for iterative solvers.
Results of applying ICO to a land 3D survey showed that regularizing the
coverage before imaging helps preserve the
amplitude information and the high frequency components of the reflectivity
function.
Furthermore, ICO provides a promising approach for reducing the costs of
3D acquisition.
time-slice
Figure 6 Time slices (0.71 s) obtained by: a) NMO-Stack of over-sampled subset, b) NMO-Stack of decimated subset, c) Un-normlized AMO-Stack, d) Normalized AMO-Stack, e) ICO partial stack using the data-space inverse, f) ICO partial stack using the model-space inverse.




 comp-inline
comp-inline
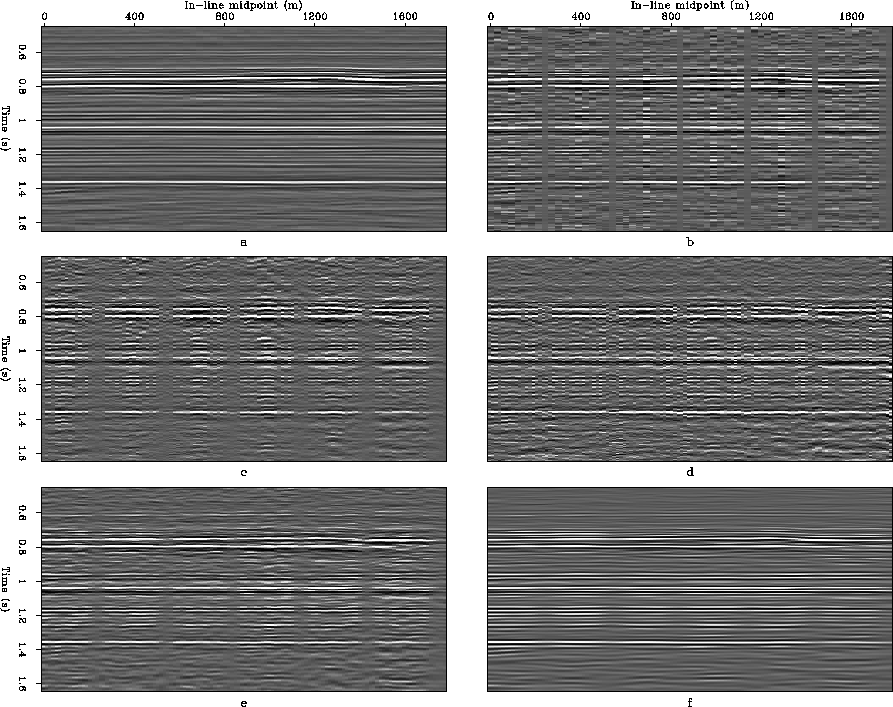
Figure 7 In-line sections at 1 km obtained by: a) NMO-Stack of over-sampled subset, b) NMO-Stack of decimated subset, c) Un-normlized AMO-Stack, d) Normalized AMO-Stack, e) ICO partial stack using the data-space inverse, f) ICO partial stack using the model-space inverse.




 comp-crossline
comp-crossline
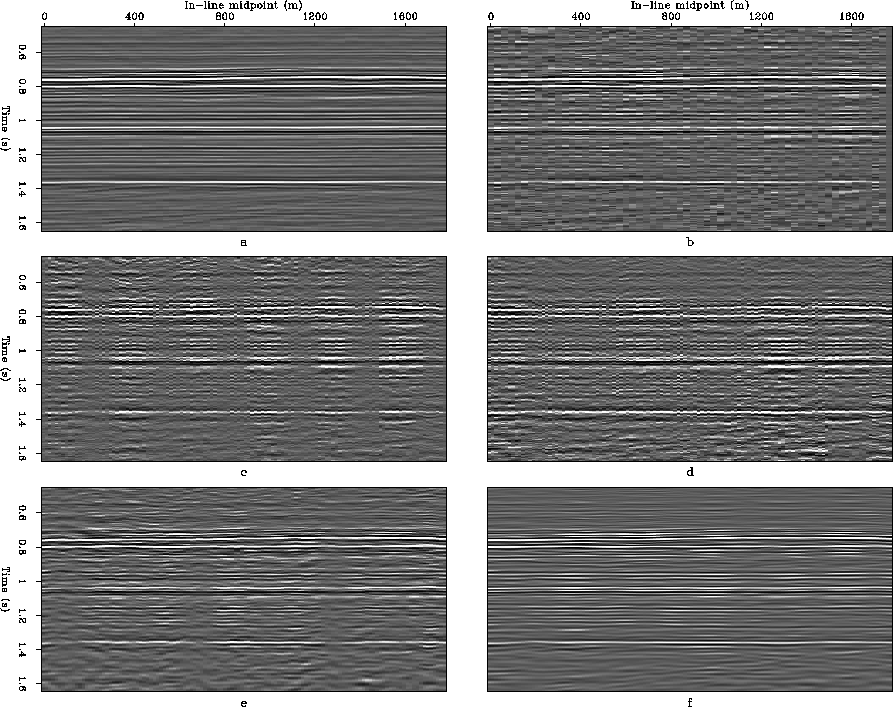
Figure 8 Cross-line sections at 1 km obtained by: a) NMO-Stack of over-sampled subset, b) NMO-Stack of decimated subset, c) Un-normlized AMO-Stack, d) Normalized AMO-Stack, e) ICO partial stack using the data-space inverse, f) ICO partial stack using the model-space inverse.




 mig920
mig920
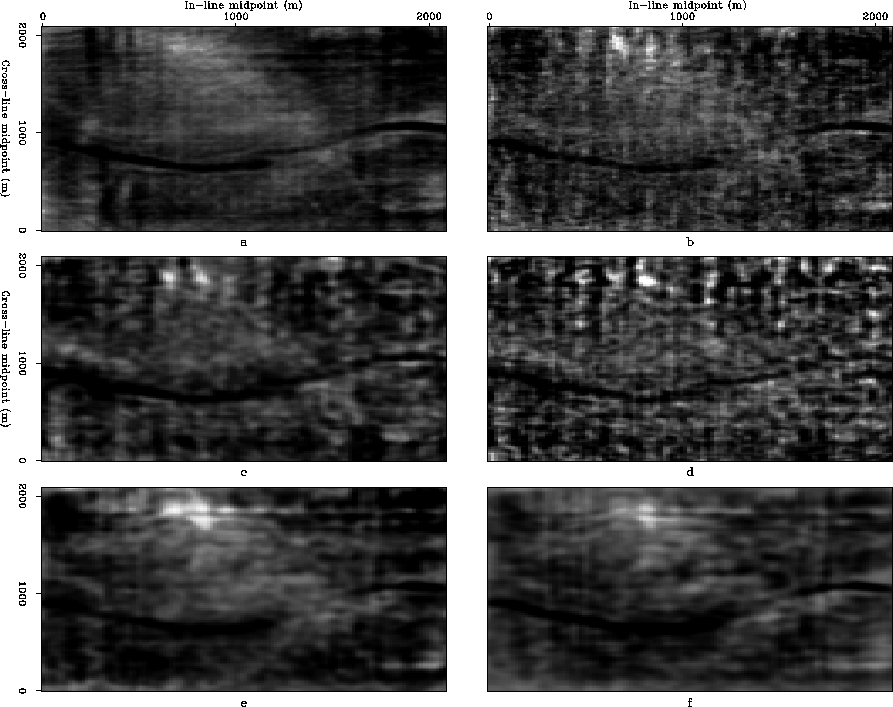
Figure 9 Depth slices at 920 m obtained by different imaging flows a) Migration of oversampled subset, b) Migration of decimated subset, c) Migration after binning, d) Migration after normalized AMO, e) Migration after ICO using data-space inverse, f) Migration after ICO using model-space inverse




 mig910
mig910
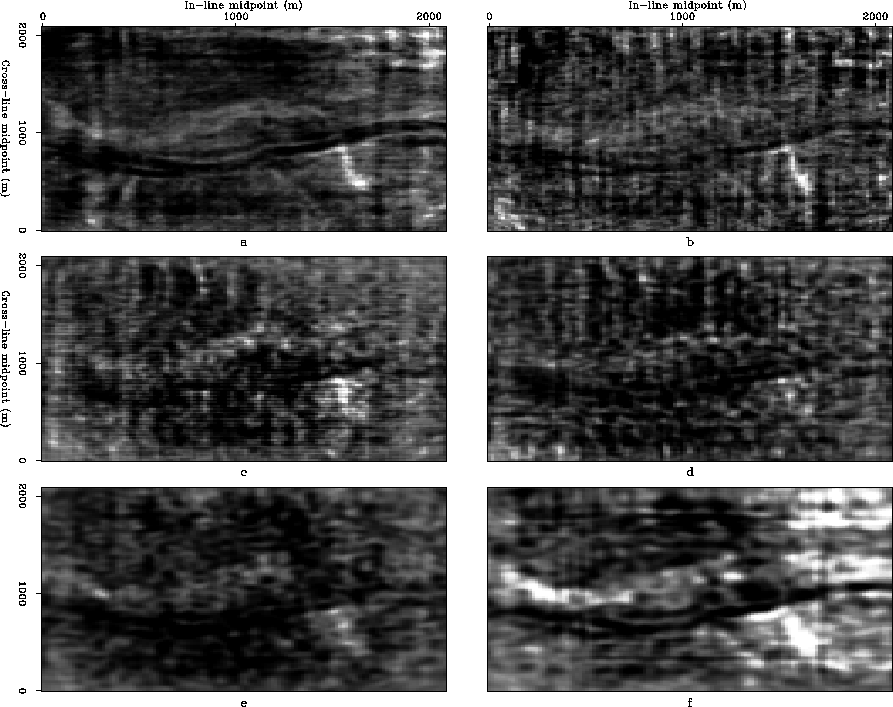
Figure 10 Depth slices at 910 m obtained by different imaging flows a) Migration of oversampled subset, b) Migration of decimated subset, c) Migration after binning, d) Migration after normalized AMO, e) Migration after ICO using data-space inverse, f) Migration after ICO using model-space inverse










Next: Derivation of integral AMO
Up: Inversion to common offset
Previous: Migration after regularization
Stanford Exploration Project
1/18/2001