




Next: Bleistein Born DMO and
Up: Integral inverse DMO
Previous: Hale DMO and its
Similar to the preceding discussion, I start the derivation for an
asymptotic inverse for Black/Zhang's DMO by recognizing the coordinate relationships,
| 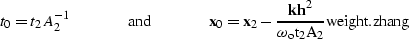 |
(29) |
The Jacobian of the change of variables in the forward DMO is given by
| 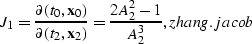 |
(30) |
which has the familiar form of Zhang's 1988 and Black's
1993 Jacobian.
Zhang based his derivations on kinematic arguments that
considered a fixed reflection point rather than a fixed midpoint. This
derivation takes into account the reflection-point smear
Black et al. (1993a); Deregowski and Rocca (1981), which means that
the input event at location 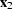 will be positioned
by DMO to the correct zero-offset location
will be positioned
by DMO to the correct zero-offset location 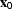 .
.
To compute the Beylkin determinant for Black/Zhang Jacobian I begin by
writing the phase function in the DMO integral kernel as
| 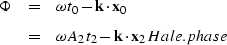 |
(31) |
| (32) |
The phase in equation Hale.phase is identical to the phase function
in Hale's DMO and, therefore, substituting for  and
and 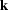 back in
omega and wave.numb and differentiating with respect to
back in
omega and wave.numb and differentiating with respect to 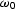 and
and 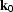 , we end up with the following expression for H-1:
, we end up with the following expression for H-1:
| 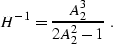 |
(33) |
Therefore, the Beylkin determinant
for Black/Zhang's DMO becomes
| 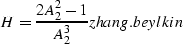 |
(34) |
which is the same as that for Hales's DMO.
Finally, by substituting back in jacob2 and accounting for the 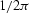 factor in the spatial Fourier transform, we obtain an expression for
the weights of an asymptotic inverse for Black/Zhang's DMO:
factor in the spatial Fourier transform, we obtain an expression for
the weights of an asymptotic inverse for Black/Zhang's DMO:
| 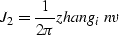 |
(35) |
These weights have been also derived independently by Paul
Fowler (personal communication).





Next: Bleistein Born DMO and
Up: Integral inverse DMO
Previous: Hale DMO and its
Stanford Exploration Project
1/18/2001
![]() factor in the spatial Fourier transform, we obtain an expression for
the weights of an asymptotic inverse for Black/Zhang's DMO:
factor in the spatial Fourier transform, we obtain an expression for
the weights of an asymptotic inverse for Black/Zhang's DMO: