




Next: INVERSE NMO STACK
Up: ITERATIVE METHODS
Previous: Setting up a generic
Now we assemble a module cgmeth for solving simultaneous equations.
Starting with the conjugate-direction module cgstep_mod
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) we insert the module matmult
we insert the module matmult ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) as the linear operator.
as the linear operator.
module cgmeth {
use matmult
use cgstep_mod
use simple_solver
contains
# setup of conjugate gradient descent, minimize SUM rr(i)**2
# nx
# rr(i) = sum fff(i,j) * x(j) - yy(i)
# j=1
subroutine cgtest( x, yy, rr, fff, niter) {
real, dimension (:), intent (out) :: x, rr
real, dimension (:), intent (in) :: yy
real, dimension (:,:), pointer :: fff
integer, intent (in) :: niter
call matmult_init( fff)
call solver( matmult_lop, cgstep, x, yy, niter, res = rr)
call cgstep_close ()
}
}
Below shows the solution to 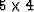 set of simultaneous equations.
Observe that the ``exact'' solution is obtained in the last step.
Because the data and answers are integers,
it is quick to check the result manually.
set of simultaneous equations.
Observe that the ``exact'' solution is obtained in the last step.
Because the data and answers are integers,
it is quick to check the result manually.
d transpose
3.00 3.00 5.00 7.00 9.00
F transpose
1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00
1.00 0.00 1.00 0.00 1.00
0.00 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
for iter = 0, 4
x 0.43457383 1.56124675 0.27362058 0.25752524
res -0.73055887 0.55706739 0.39193487 -0.06291389 -0.22804642
x 0.51313990 1.38677299 0.87905121 0.56870615
res -0.22103602 0.28668585 0.55251014 -0.37106210 -0.10523783
x 0.39144871 1.24044561 1.08974111 1.46199656
res -0.27836466 -0.12766013 0.20252672 -0.18477242 0.14541438
x 1.00001287 1.00004792 1.00000811 2.00000739
res 0.00006878 0.00010860 0.00016473 0.00021179 0.00026788
x 1.00000024 0.99999994 0.99999994 2.00000024
res -0.00000001 -0.00000001 0.00000001 0.00000002 -0.00000001
EXERCISES:
-
One way to remove a mean value m from signal
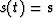 is with the fitting goal
is with the fitting goal 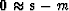 .What operator matrix is involved?
.What operator matrix is involved?
-
What linear operator subroutine from Chapter
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) can be used for finding the mean?
can be used for finding the mean?
-
How many CD iterations should be required to get the exact mean value?
-
Write a mathematical expression for finding the mean by the CG method.





Next: INVERSE NMO STACK
Up: ITERATIVE METHODS
Previous: Setting up a generic
Stanford Exploration Project
2/27/1998
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) we insert the module matmult
we insert the module matmult ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) as the linear operator.
as the linear operator.