|
|
|
|
Polarity preserving decon in ``N log N'' time |
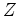 -transforms.
Data length must be a power of two.
Subroutine kolmogoroff below was taken from my book PVI,
converted from energy spectra to amplitude spectra.
An insert in the middle
implements the innovation of this paper;
it diminishes the asymmetric part of
-transforms.
Data length must be a power of two.
Subroutine kolmogoroff below was taken from my book PVI,
converted from energy spectra to amplitude spectra.
An insert in the middle
implements the innovation of this paper;
it diminishes the asymmetric part of 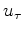 near
near 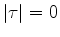 .
A cosine squared weight was arbitrarily chosen.
The suppression range was chosen from the origin to half way to an expected bubble on 4ms data.
.
A cosine squared weight was arbitrarily chosen.
The suppression range was chosen from the origin to half way to an expected bubble on 4ms data.
While looking at the code you might notice that you also have the ability to taper large lags to shorten your filter response. This might be useful when you want to crop off downgoing multiples from your source waveform. It would also be helpful when you have insufficient data to be estimating long source waveforms.
subroutine kolmogoroff( n, cx) # Spectral factorization.
integer i, n # input: cx = amplitude spectrum
complex cx(n) # output: cx = FT of min phase wavelet
integer lag
real weight, asym
do i= 1, n
cx(i) = clog( cx(i) )
call ftu( -1., n, cx)
do i= 2, n/2 {
cx(i) = cx(i) * 2.
cx(n-i+2) = 0.
}
# BEGIN stuff added to remove a little of the asymmetric part.
lag = 15 # lag = 60ms/4ms where 60ms is half way to bubble.
do i = 2, lag {
asym = (cx(i) - cx(n-i+2))/2.
weight = cos( .5* 3.1416 * (i-1.)/(lag-1.))**2
cx(i) = cx(i) - weight * asym
cx(n-i+2) = cx(n-i+2) + weight * asym
}
# END stuff added to remove a little of the asymmetric part.
call ftu( +1., n, cx)
do i= 1, n
cx(i) = cexp( cx(i))
return; end
subroutine ftu( signi, nx, cx )
# complex fourier transform with traditional scaling
#
# 1 nx signi*2*pi*i*(j-1)*(k-1)/nx
# cx(k) = -------- * sum cx(j) * e
# scale j=1 for k=1,2,...,nx=2**integer
#
# scale=1 for forward transform signi=1, otherwise scale=1/nx
integer nx, i, j, k, m, istep, pad2
real signi, arg
complex cx(nx), cmplx, cw, cdel, ct
do i= 1, nx
if( signi<0.)
cx(i) = cx(i) / nx
j = 1; k = 1
do i= 1, nx {
if (i<=j) { ct = cx(j); cx(j) = cx(i); cx(i) = ct }
m = nx/2
while (j>m && m>1) { j = j-m; m = m/2 } # "&&" means .AND.
j = j+m
}
repeat {
istep = 2*k; cw = 1.; arg = signi*3.14159265/k
cdel = cmplx( cos(arg), sin(arg))
do m= 1, k {
do i= m, nx, istep
{ ct=cw*cx(i+k); cx(i+k)=cx(i)-ct; cx(i)=cx(i)+ct}
cw = cw * cdel
}
k = istep
if(k>=nx) break
}
return; end